For centuries, the gentle secret of Egyptian blue, the world’s first synthetic pigment, lay tenderly hidden in the sands of time. This radiant, breathtaking blue, lovingly crafted by ancient Egyptians for their art and sculptures, has been reborn through the caring hands of modern scientists. In a heartwarming breakthrough, researchers have joyfully recreated this ancient hue, opening pathways to innovative technologies, artistic wonders, and even new commercial possibilities. With kindness, this revival connects us to our ancestors’ creativity, inspiring a vibrant, shared future filled with beauty and hope.

In this article, we’ll explore the significance of Egyptian blue, the methods used by scientists to recreate it, its historical importance, and how this pigment might play a role in today’s world.
Scientists Finally Recreate Egyptian Blue
| Key Point | Details | Source/Link |
|---|---|---|
| Egyptian Blue’s Origins | Egyptian blue is the oldest known synthetic pigment, created more than 5,000 years ago in Egypt. | Washington State University |
| Recreation Process | Scientists from Washington State University and other institutions have successfully recreated the pigment using modern techniques. | Carnegie Museum of Natural History |
| Scientific Importance | The pigment is not only a marvel of ancient chemistry but also exhibits photoluminescence, which can be used in modern technologies. | Smithsonian Magazine |
| Modern Applications | The pigment’s properties are now being explored in fields like materials science, medical imaging, and even anti-counterfeit technology. | Popsci.com |
The heartfelt revival of Egyptian blue marks a radiant milestone, touching not only archaeology and art history but also the gentle frontiers of modern science and technology. This vibrant pigment, once lovingly used to adorn pharaohs’ tombs, now sparkles with potential to nurture advancements in technology, security, and medicine. With care, the story of Egyptian blue weaves a beautiful reminder that ancient creativity can continue to inspire profound, compassionate impacts, connecting humanity across time to a brighter, more innovative future.

What Is Egyptian Blue?
To really understand the significance of this breakthrough, we first need to know what Egyptian blue is.
Egyptian blue is a vibrant blue pigment made by heating a mixture of silica (sand), copper compounds, such as malachite or azurite, lime, and an alkali substance, usually natron or plant ash. The temperature needed to create the pigment was around 1,000°C (1,832°F), and the result was a copper calcium silicate compound (CaCuSi₄O₁₀) known as cuprorivaite.
This pigment was widely used by ancient Egyptians for everything from wall paintings to ceremonial objects, and it was often associated with the gods and the afterlife due to its intense, celestial blue color. In fact, Egyptian blue was so prized that it continued to be used by the Romans, though its production eventually declined during the medieval period and was lost to history for hundreds of years.
The Modern Recreation of Egyptian Blue
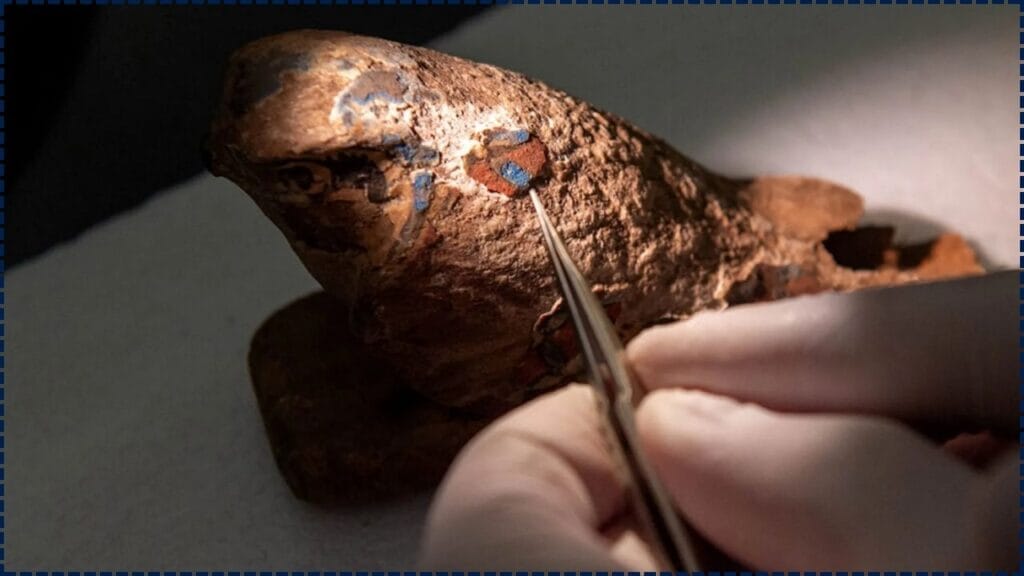
Fast forward to today, where modern scientists have successfully recreated this ancient pigment. The team behind this breakthrough comes from Washington State University, in collaboration with the Carnegie Museum of Natural History and the Smithsonian Institution’s Museum Conservation Institute. These researchers used a combination of traditional and modern methods to bring Egyptian blue back to life, using thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction, and photoluminescence imaging to study the pigment’s chemical structure and physical properties.
What makes this recreation so remarkable is that it wasn’t just about reproducing the color. The team went above and beyond by experimenting with various recipes and methods of heating to reproduce the unique glow and texture of Egyptian blue. The color variability was an important part of the research, as scientists discovered that the blue could vary depending on the ratio of blue-colored components in the pigment, as well as the cooling rate after heating.
In fact, slow cooling, such as burying the pigment mixture in sand, created richer, deeper blues, a detail that mirrors the likely techniques used by ancient Egyptians.
Why Egyptian Blue Is More Than Just a Pretty Color
While Egyptian blue was primarily used for its aesthetic value in art and decoration, it turns out that the pigment’s properties are incredibly useful in modern technologies. One of the most interesting aspects of Egyptian blue is its ability to emit near-infrared light when exposed to visible light. This phenomenon, known as photoluminescence, makes the pigment an excellent material for applications such as:
- Anti-counterfeit technologies: Egyptian blue’s unique ability to emit infrared light makes it ideal for use in security inks. These inks can be used on everything from currency to documents to protect against fraud.
- Biomedical imaging: The pigment’s photoluminescent properties make it useful for imaging applications. Researchers are now looking into using Egyptian blue in medical imaging techniques for non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring.
- Materials science: Scientists are exploring Egyptian blue’s crystal structure, which shares similarities with high-temperature superconductors, making it a promising candidate for future materials in advanced technology fields.
- Environmental applications: Another possibility is using Egyptian blue for environmentally-friendly applications. Due to its ability to absorb and reflect specific wavelengths of light, it could be used in solar panels or building materials that reduce energy consumption by reflecting infrared light.
The Historical and Cultural Significance of Egyptian Blue
It’s easy to dismiss a color as just another pigment, but Egyptian blue holds a special place in history, particularly when it comes to understanding the ancient Egyptian world.
The Egyptians didn’t just use this pigment for decoration—they used it to convey symbolic meanings. The color blue was closely associated with the gods, particularly Horus, the god of the sky. In fact, many depictions of Horus and other deities were painted in Egyptian blue to emphasize their divine nature. Moreover, the pigment was often used in tombs and funerary objects, symbolizing the eternal life the Egyptians hoped to achieve in the afterlife.
The material itself, made from natural resources, showed the Egyptians’ deep knowledge of chemistry and craftsmanship. Its creation demonstrated an understanding of high-temperature chemistry—a level of expertise that many modern scientists find impressive even by today’s standards.
How Did Scientists Recreate Egyptian Blue?
So, how did scientists actually recreate this ancient pigment? The process involved several key steps:
1. Research and Experimentation
Scientists began by examining ancient artifacts that contained Egyptian blue using advanced techniques like X-ray diffraction to analyze their molecular structure. They also studied historical texts and chemical recipes to better understand the methods used by ancient Egyptians.
2. Creating Different Recipes
Researchers created multiple variations of the pigment by adjusting the ratio of ingredients such as copper, lime, and alkali. This experimentation helped the team recreate the pigment’s unique coloration and texture.
3. High-Temperature Heating
The pigment is created through high-temperature heating. To replicate the blue, the team subjected the mixture to 1,000°C in a furnace. Different cooling rates were used to see how they affected the pigment’s final color.
4. Analyzing the Results
After synthesizing the pigment, the researchers used techniques like thermal analysis and photoluminescence imaging to analyze the properties of the pigment and compare it to ancient samples. This helped them determine the chemical composition of the pigment and its luminescent properties.
Related Links
8 Proven Strategies to Stay Financially Afloat When Times Get Tough
European Space Agency Sends Classical Music Into Space—Here’s Why
Practical Applications of Egyptian Blue
While the modern world might not be filling tombs with Egyptian blue any time soon, the pigment is being explored for a variety of uses:
- Art Restoration: The recreated pigment can be used in restoring ancient artifacts. The ability to match Egyptian blue exactly ensures that restorers can recreate original works of art with high accuracy.
- Material Science: Egyptian blue’s unique properties make it a candidate for use in advanced technologies, from data storage devices to energy-efficient building materials.
- Security and Anti-Counterfeiting: The luminescent properties of Egyptian blue make it valuable for security applications. Its use in authenticating documents, currency, and high-value goods could help reduce counterfeiting.
- Solar and Energy Efficiency: Egyptian blue’s ability to reflect specific wavelengths of light could make it ideal for creating energy-efficient materials in construction and renewable energy industries. It could be used in cool roofs or solar panel coatings, potentially reducing the heat absorption in buildings.
FAQs
1. What was Egyptian blue used for in ancient Egypt?
Egyptian blue was used in a variety of contexts, including tomb paintings, ceremonial objects, and statues. It was often associated with the gods and the afterlife.
2. How did scientists recreate Egyptian blue?
Scientists recreated Egyptian blue by experimenting with the original ingredients and using high-temperature heating methods. They also studied ancient artifacts to understand the pigment’s composition and characteristics.
3. What is the significance of Egyptian blue’s photoluminescent properties?
The pigment’s ability to emit near-infrared light when exposed to visible light opens up applications in biomedical imaging, anti-counterfeit technology, and materials science.
4. How does Egyptian blue compare to other blue pigments?
Egyptian blue is unique due to its luminescent properties. Unlike modern blue pigments, it emits near-infrared light, making it distinct in both its physical properties and its applications.
5. What are some modern uses for Egyptian blue?
Modern uses of Egyptian blue include applications in art restoration, anti-counterfeiting technologies, biomedical imaging, materials science, and even energy-efficient building materials.